Acoustic Calculations
Propagation
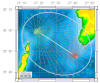 A
ray-theoretic code has been developed for the calculation of the acoustic field,
in particular transmission loss versus range and depth, and intensity of the
scattered field at the bottom versus range. 3D coverage is obtained by solving
the propagation problem along 36 vertical range-dependent sections extending
radially around the source location in angle steps of 10°, as well as 36 similar
sections around the receiver location .
A
ray-theoretic code has been developed for the calculation of the acoustic field,
in particular transmission loss versus range and depth, and intensity of the
scattered field at the bottom versus range. 3D coverage is obtained by solving
the propagation problem along 36 vertical range-dependent sections extending
radially around the source location in angle steps of 10°, as well as 36 similar
sections around the receiver location .
Reverberation
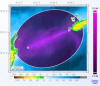 The
bistatic reverberation is calculated by combining the transmission loss and
scattered field intensity results provided by the propagation code. The
contributions of the scattered field at the bottom are integrated along ellipses
having the source and receiver locations as focal points, taking into account
the directional characteristics (directivity pattern, steering angle) of the
receiver.
The
bistatic reverberation is calculated by combining the transmission loss and
scattered field intensity results provided by the propagation code. The
contributions of the scattered field at the bottom are integrated along ellipses
having the source and receiver locations as focal points, taking into account
the directional characteristics (directivity pattern, steering angle) of the
receiver.
Directivity
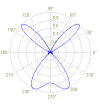 In
the current version of the system the acoustic source is assumed to be
omnidirectional while the reception is considered to be directional, and subject
to beam steering. The directivity pattern and the resulting directivity index is
calculated at any steering angle of the array by applying spatial filtering –
beamforming.
In
the current version of the system the acoustic source is assumed to be
omnidirectional while the reception is considered to be directional, and subject
to beam steering. The directivity pattern and the resulting directivity index is
calculated at any steering angle of the array by applying spatial filtering –
beamforming.
Probability of Detection
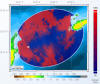 Using
the results of the above calculations and the operational characteristics of the
involved platforms (source, target, receiver) the signal-to-noise and
signal-to-reverberation ratios at the beamformer output are calculated for each
target location. Then the probability of detection is calculated using receiver
operating characteristics (ROC curves) for energy or matched-filter detection.
Using
the results of the above calculations and the operational characteristics of the
involved platforms (source, target, receiver) the signal-to-noise and
signal-to-reverberation ratios at the beamformer output are calculated for each
target location. Then the probability of detection is calculated using receiver
operating characteristics (ROC curves) for energy or matched-filter detection.